Introduction
The opening on the IFRS standards of the Moroccan accounting is made of 2007 through the obligation to credit institutions to publish their consolidated financial statements in international standards from 2008 onwards and the option permitted to non-financial private and public businesses to use the new repository as the basis of consolidation from 2007 onwards.
The “value relevance” of the accounting data has been the subject of an abundant literature, Bartov et al. , 2005 ; Barth et al. , 2008 ; Hung and Subramanyam, 2007, Van Tendeloo and Vanstraelen, 2005, have sought to demonstrate the superiority in terms of quality of the accounting data prepared in accordance with the international standards IFRS compared to local standards.
While several studies have examined the effects of IFRS adoption worldwide, the empirical evidence from Morocco is sparse (Ahsina and al, 2014)
Indeed, most of these studies have been carried out in developed markets much less in emerging ones, such as the one in Casablanca characterized by a small number of companies listed on a low volume of exchanges, or the usefulness of this article. The question that is posed in this research is to know, beyond the motivations, what has pushed the Moroccan enterprises to adopt the IFRS (Ahsina, 2012), if the new repository is the pledge of a superior quality to the Moroccan national repository.
This article tries to measure the value relevance of IFRS without associating it with external data accountants (stock and financial profitability).
Based on a sample of 9 companies listed on the Casablanca stock exchange, and using the methodology of studies of association, our goal is to check if the international accounting standards are superior in terms of informational content to the Moroccan accounting standards that meet the information needs of investor’s fellows.
After an overview of the literature on the quality of accounting and the superiority of the IFRS standards (section 1), the research methodology will be presented (section 2), and then the results of the research (section 3) and we will finally discuss the results and the main extensions of the research (section 4).
Superiority of IFRS: A Controversial Literature
The accounts must record the accounting data based on market prices since they reflect the result of the interaction of supply and demand of rational investors in an efficient market.
Thus, based on financial and accounting indicators, investors evaluate the company’s shares which will enable them to make decisions including those for the purchase or sale of shares in the financial markets.
However, many criticisms have been leveled against the traditional model of accounting: principles which are unrealistic convey no absolute information, and there are many subjective choices on the part of leaders.
The application of fair value allows businesses to have the financial statements more relevant to the needs of investors.
Indeed, the principles of historical cost, prudence, consistent accounting methods, and other principles of traditional accounting system did not allow the company to reflect the economic reality and follow developments of the financial market.
To respond to these criticisms, many research called “Value Relevance Studies” were conducted.
Ball and Brown (1968) and Beaver (1968) deserve the credit of being considered the founding studies of informational value of accounting figures. Ball and Brown studied the information content of earnings, and demonstrated that they are correlated with the market price. Beaver, meanwhile, had studied the informational relevance by observing the reaction of dung beetles price and volume of transactions following the publication of annual reports.
However, considering that the first study that has literally used the term “value relevant” to describe the association between accounting numbers and value of companies that is of Amir et al. (1993).
However, it should be noted that the research work on the value relevance diverge jobs that are advocating superiority of IFRS by local standards (A) or no significant difference between the informational content of two standards (B), or conversely to the superiority of local standards (C).
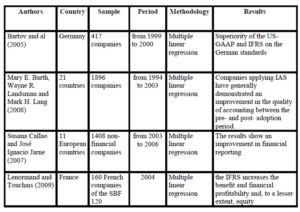
Table 1: the superiority of IFRS
Among the most influential research in terms of study of the relevant value (Table 1) IFRS, Bartov et al (2005), Barth et Ali (2008), Callao and Jarne (2007), and The Norman Touchais (2009) show that the adjustment of profits by local standards to IFRS increases the informational relevance of accounting numbers.
Table 2: No significant differences between local GAAP and IFRS
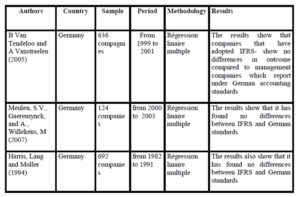
Other research studies, such as those of Meulen, Gaeremynck and Willekens (2007) find that IFRS and US GAAP have some similarity in their informational pertinence.
The study by Harris, Lang and Moller (1994) also shows that the explanatory power of the profits of listed companies on the German market is comparable to that found on the same sample company listed on the American market.
Unlike the work of Bartov et al in a study, Subramanyam Hung (2007) finds that the informational relevance of equity under IFRS is lower than the values established in accordance with German local standards. Schiebel (2007) reaches the same conclusion on a sample of 24 German companies over the period 2000-2004.
Finally, based on this brief literature review, we can say that the implicit hypothesis is that there would be a superiority of IFRS on national standards, however, this hypothesis is controversial.
What about in Morocco? , It is therefore interesting to corroborate these results against the Moroccan accounting standards.
Research Design and Methodology
Our research includes assessing which of the two IFRS or national standards applied to the Moroccan financial market and the association between accounting figures (benefits and equity) and stock returns is the most important?
This work is based on a model developed by Amir et al 1993, Barth and Clinch 1996; Harris and Muller 1999. This is to achieve association studies between market values and financial information from the French standards by incorporating the differential amount resulting from the application of IFRS.
Indeed, according to Barth et al. (2001) models of price and performance meet up questions. The first is concerned with events into prices while the latter seeks to identify what may reflect changes in value over a given period of time.
After a presentation of the financial models of association between profitability and stock prices, the description of our research sample will be presented.
Association model based on securities prices
Pi,t = a0+a1BPAi,tM +a2BPAi,tDIF+a3CPPAji,tM+a4CPPAji,tDIF+ εi,t
with: – Pi, t: the company share price of the i at the end of year t,- BPAI, tM: earnings per share by Moroccan standards of the company in year t,- BPAI, Tdif: the difference in earnings per share between IFRS and the Company’s Moroccan repository i t, – CPPAji, tM: equity per share Adjusted earnings per share by Moroccan standards of the company i at the end of the year t, – CPPAji, Tdif: Unlike equity per share adjusted between IFRS and the Company’s Moroccan repository i at the end of the year t. If we obtain a2 and a4 coefficients significantly different from 0, we can say that the adoption of IFRS provides additional information for the investor.
Association model based on yields
Ri,t = b0+b1BPAi,tM + b2∆BPAji,tM+ b3BPAi,tDIF+ εi,t
Pi,t-1 Pi,t-1 Pi,t-1
With: – Ri, t: dividend yield of the company i in year t,- BPAji, t: earnings per share by Moroccan standards of the company i in year t4,- ΔBPAji, t: the change in earnings per share in Moroccan standards of the company i in year t,- BPAI, Tdif the difference in earnings per share between IFRS and the Company’s Moroccan repository i t. If IFRS provide the additional information, the coefficient b3 should be significantly different from 0.
Sample Description
The data on the consolidated financial statements for the year of IFRS adoption were obtained either from the Casablanca Exchange database or that of the AMF or by direct solicitation of finance departments of the companies concerned.
However, it was from 2007 that has been most transition to IFRS. Indeed it is from this year that the AMF and the Stock Exchange have increased their monitoring of consolidated publications of Moroccan enterprises and encouragement of transition to IFRS.
The sample was initially composed of 75 Moroccan companies listed on the Casablanca Stock Exchange that have reported under transition- exercise their consolidated financial statements in both the Moroccan accounting standards and under IFRS.
Table 3 : Incorporation our sample
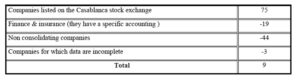
Consistent with the literature on earnings management and the theory of value relevance (Callao et al, 2007; Van Tendeloo and Vanstraelen, 2005; Vander Bauwhede, 2001), we eliminated all financial institutions and non- consolidating companies in our sample, thus ensuring greater uniformity of companies included in the sample.
Results
Before presenting the results of the models tested, let’s look at the key variables in order to analyze how the adoption of IFRS leads to significant changes in the amounts of equity and minor on profits.
Descriptive statistics
Table 4: Descriptive statistics of financial and stock market variables MAS and IFRS
(in Thousand Moroccan dirham)
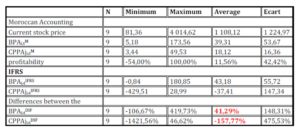
In line with several studies (Bartov, Barth and Le Normand etc.), we observe that the adoption of the international standard is accompanied by a significant increase in earnings per share (41.29 % on average) and decreased much more significant equity (-157.77 % on average).
Similarly, the decrease in equity was also confirmed by researchers work, and Touchais The Norman (2009) 160 companies in the SBF 250, Mazars (2005) and FinHarmony (2005) on the French CAC 40.
These results indicate that the adoption of IFRS by listed companies to the Moroccan Casablanca stock exchange resulted in differentiated impacts on profits and equity.
The analysis of the relevance of IFRS compared to Moroccan local standards will be developed further in the next paragraph.
The value relevance of accounting standards by pricing models
We study the value relevance of both repositories analyzing associations between stock prices and equity and profits in Moroccan and international standards.Table 5 presents the modeling results of the securities prices related to financial data.
Table 5: Price Model Summary of securities by the financial data
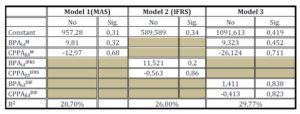
We note that the share price is positively associated with income (coefficient 9.81) and negatively to equity (-12.97 coefficient); however, these coefficients are not statistically significant at the 5% level.
We also note that the Moroccan accounting standards are more relevant to IFRS, since the explanatory power of model1 measured by the R2 (28.7%) is higher than that of Model 2 ( 26%) of IFRS .
The introduction of variables measuring the differences in amounts arising from the adoption of IFRS (Model 3) causes a slight increase in the coefficient of determination R2 , which rose from 28.7 % to 29.77 %, or 1.07% of variation.
Similarly, the difference in earnings per share with IFRS (BPAI, TDIF) is small and not significant. So, we can say that the introduction of IFRS international standards does not provide additional information content to the Moroccan accounting standards.
The model on profitability and the results presented in Table 5 are meant to validate these findings.
The value relevance of accounting standards by the profitability models
In line with Amir et al (1993), this model shows that earnings per share in the Moroccan repository are not strongly associated with stock market performance, the R2 determination coefficient is 9.09%.
Likewise, we found no statistically significant relationship between the change in earnings and dividend yield.
The introduction of differential earnings per share provided by IFRS leads to a slight increase in R2 (0.32%), which is not statistically significant. Moreover, this variable has a negative coefficient indicating that IFRS do not provide extra information to the Moroccan standards.
In line with van Tendeloo H et al (2005), these results validate the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between Moroccan local standards and international standards.
Conclusion and Discussion
The objective of this research was to know if the new international repository is the pledge of a superior quality to the national repository of Morocco. Based on a sample of 9 companies listed on the stock exchange of Casablanca, we have adopted an empirical approach in two steps: firstly, a model based on the price of the shares has been tested, and then we have tested a model based on the stock performance.
The results emerged from the study suggest that the relevance of information of IFRS is low for the two models. The R2 being below 30% for the first model and to 10% for the second model. The obligation to adopt the IFRS standards imposed by the authority of the financial markets (CDVM) and the Central Bank of Morocco is not timely since it has not led to the production of financial information more relevant and of good quality.
However, these results must be taken with caution in view of the limits and the prospects of the research.
The limits of Research
Among the limits of our research, the small size of our sample is a handicap to generalize the scope of the results to the entire population of companies listed on the stock exchange of Casablanca.
Another important limitation to be able to properly assess the impact of the IFRS standards is that it takes a certain time (on average two years) to pronounce actually on the adoption of this repository.
Similarly, association studies suffer from several limitations which can be summarized as follows:
-Of Institutional factors (economic, legal and political) specific to the country’s environment are not taken by the association model, which reduces its explanatory power.
-The Methodology of value relevance is the subject of criticism for some time (Holthausse and Watts (2001); Ronen (2001), it would be interesting to confirm and complement these results if adopting a different methodology.
Commissioning Perspective search results
This research presents a contribution at several levels for both managers and accountants. The introduction of IFRS has no significant impact on the quality of accounting numbers. It is not wise to implement this standard which requires substantial /resources in terms of human and financial resources.
Extensions Search
Our research could be enriched by the consideration of the economic sectors that we have not considered.
Loan of eight years after the adoption of IFRS, what about the degree of their additional relevance?
Indeed, studying the value relevance after 2007 could give us information about the quality of the national reference system related to international standard, and on issues of harmony and upgrade of our local repository.
References
1. Ahsina K, (2012).Implementing IAS-IFRS in the Moroccan context: an explanatory model.International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2
Publisher – GoogleScholar
2. Ahsina K, Taouab O, Cherqaoui MB (2014). L’impact de l’adoption des IFRS sur les sociétés cotées à la bourse de Casablanca : une étude exploratoire . La Revue Gestion et Organisation N°6.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
3. Amir, E., Harris, T., & Venuti, E. (1993). A Comparison of the Value-Relevance of US versus non-US GAAP Accounting Measures Using Form 20-F Reconciliations. Journal of Accounting Research,31, 230-264.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
4. M. Barth , Wayne R. Landsman, Mark Lang, and Christopher Williams (2008). International ccounting Standards and Accounting Quality. Journal of Accounting Research, 2008, vol. 46, issue 3,pages 467-498
Publisher – GoogleScholar
5. Bartov, E., Goldberg, S.R., Kim, M. (2005). Comparative value relevance among german, US and international accounting standards : A german stock market perspective. Journal of Accounting,Auditing and Finance 20 (2) : 95-119. GoogleScholar
6. Boukari , M., Richard, J., (2007). Les incidences comptables du passage des groupes français cotés aux IFRS. Comptabilité contrôle audit, Vol. Thématique, décembre, pp.155-170
Publisher – GoogleScholar
7. Francis, J., & Schipper, K. (1999). Have financial statements lost their relevance? Journal of Accounting Research, 37, 319—352.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
8. Harris, T., Lang, M., Moller, H. (1994). The Value Relevance of German Accounting Measures: An Empirical Analysis. Journal of Accounting Research, Vol. 32, p.187-209.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
9. Hung, M., Subramanyam, KR. (2007). Financial Statement Effects of the Adoption of International Accounting Standards: The Case of Germany. Review of Accounting Studies 12(4), p. 623-657.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
10. Raoudha Trabelsi., (2013). Vers un dispositif d’appréciation de la pertinence des IFRS dans un contexte pré- Implémentation International. Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies. Vol. 3 No. 3 July 2013, pp. 626-650.
11. S Callao, J I. Jarne, J A. Laınez (2007). Adoption of IFRS in Spain: Effect on the comparability and relevance of financial reporting. Journal of International Accounting, Auditing and Taxation. 16 (2007) 148—178.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
12. Schiebel, A. (2007). Value relevance of German GAAP and IFRS consolidated financial reporting: An empirical analysis on the Frankfurt stock exchange. Vienna University of Economics andBusiness Administration, working paper.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
13. Meulen, S.V., Gaeremynck, A., Willekens, M. (2007). Attribute differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS earnings: An exploratory study. The International Journal of Accounting, Vol. 42, 2, p. 123- 42.
Publisher – GoogleScholar
14. Tendeloo, B. and A. Vanstraelen (2005). “Earnings Management Under German GAAP Versus IFRS”, European Accounting Review, 14 (1), pp. 155-180.
Publisher – GoogleScholar