Introduction
National projects are a key trend and a special strategic Russian instrument for stimulating the economic growth in the Russian economy. The idea of national projects in Russia was born as a result of the search for the new strategic points of growth and development of the Russian economy that can not only provide the economy with a new breakthrough socio-economic level of development, but also improve the quality of life of Russian citizens, creating conditions and opportunities for self-realization and development of each Russian resident. National projects were developed during 2018 and currently include sectoral goals and objectives, the list of federal projects, the expected results of their implementation and the parameters of financial support in the context of sources of budget and non-budgetary sources of funding. To ensure the unity of the state strategic planning system, the list of Federal projects is included in the sub-program elements of the relevant state programs of the Russian Federation. In 2019-2024, it is planned to allocate more than 25.7 trillion rubles for national projects, of which 29.1% are non-budgetary sources; 51% – means of the Federal budget of the Russian Federation and about 20% – means of regional budgets and state extra-budgetary funds. The main task of the national project financing system in the country is to develop new schemes and mechanisms for financing national projects that can optimally combine different conditions and sources of financing, as well as attract significant resources to improve the quality and level of the socio-economic development and life in the country.
Objectives of the Study
The broad objective of the study is to examine the system and methods of financing national projects, analyze the effect of their implementation on the Russian economy and think about the structure between different budget and extra-budgetary sources of financing national projects in various sectors of the economy in Russia.
Literature Review
National projects, as a special Russian instrument based on the long-term socio-economic development plans of Russia, are an instrument for achieving its goals, and are oriented on a program-targeted approach. Preconditions for the introduction and use of program-targeted approaches to budgeting in the implementation of national projects in the framework of state programs began in Russia in the early twentieth century, long before the development of national projects themselves. During this time, the government of Russia has rebuilt the system of planning and forecasting socio-economic indicators in the country, as well as the sectoral development of the economy, in order to fully assess the effectiveness of public expenditures from the budget in relation to the main parameters of the economic development. However, the process of forming an integrated system for managing state and municipal finances at all levels of the state’s budget system is still incomplete. A serious budget reform based on a program-targeted approach has been carried out, which has made it possible to build a budget process in Russia and link the achievement of efficiency between strategic goals, priority tasks of social and economic development and state programs, as well as national and federal projects. National projects in the system of state and municipal finance have become a key mechanism that allows linking strategic and budget planning, increasing budget transparency at all levels of the country’s budget system.
A special feature of national projects in Russia is the presence of a special management system that provides for accelerated decision-making management and the allocation of significant financial resources from the federal budget of the Russian Federation for their implementation.
Theoretical Review
The development of public finance management in the RF in recent 10 years is due to the following trends:
– Increasing the independence of the Executive authorities of the Russian regions,
– Reducing the dependence of the consolidated budgets of Russian regions on financial assistance from the federal budget of the Russian Federation,
– Developing program-targeted methods of public finance management,
– Improving the quality of regional and local financial management.
The transition to program-targeted methods of funding the state budget has been a general global trend in the past decades to improve the system of public finance management. The program budget, in many countries of the world economy, is the main mechanism for financing national projects in order to effectively spend funds on solving socio-economic problems of regional development.
The use of software instruments makes it possible to increase the flexibility of budget resources management in achieving strategic goals of economic development, and helps to minimize costs and improve the efficiency of providing all types of budget services. Within the framework of program and target planning, the financing of major national projects is implemented by developing a set of measures to equalize disparities in the socio-economic development of various territories and, as a result, to achieve the set goals and objectives laid down in national projects. Results-based management is considered an effective instrument for the public finance when the process of its implementation takes place within the framework of changes in the system of public finance management, development of strategic planning, and reform of budget powers and functions of government authorities. All these changes have been taking place in the budget sphere in Russia since the 2000s. They have created a good platform for launching a system of financing national projects in Russia and, as a result, achieving strategic goals and objectives of socio-economic development.
Prerequisites for implementing the system of financing national projects based on the program-targeted method in the budget process factors include:
- International reserves accumulated during the 2000s played a role, but were almost exhausted by 2014, and risks are increasing;
- Spending in the 2000s increased significantly, but without linking to priorities, there was bargaining for resources and erosion of budget discipline;
- Incentives to increase budget expenditures were maintained, and conditions were not created for improving the efficiency of budget expenditures;
- Strategic planning was loosely linked to budget planning, and the structure and dynamics of expenditures were loosely linked to public policy goals;
- There was no assessment of the effect of public policy instruments (budget, tax, tariff, customs, regulatory regulation);
- Planning of program and non-program expenditures, as well as capital and current expenditures were not methodologically linked.
The main issue in the course of financing national projects based on the principles of program-targeted budgeting remains the qualitative improvement of the unified system of performance indicators and its subsequent integration into the budget process. Most countries that have implemented programmatic budgeting have difficulty using performance indicators correctly. These problems include the following issues:
- Measuring the parameters of indicators based on their goals of national projects;
- Obtaining the necessary volume of high-quality statistical data for their analysis;
- Developing a system of indicators for accounting for data of individual activities.
It is widely known the most common model worldwide (especially in the OECD countries, the USA, Canada, Australia and UK) is the budgeting model (or «direct budgeting» model), which takes into account performance when budget funds are linked to either planned indicators or actual results. The application of this model implies a budget in the program format and specification of goals through indicators of expected results. Actual results are of key importance in the process of prioritizing the distribution of financial flows for the next year, but they do not affect the process of determining the amount of budget funds allocated.
In Russia, a demonstration model of program budgeting is practiced, which has the main reference point in the form of the final result. At the same time, the main feature of this model is the lack of connection between information about results and financing, since the indicators of final results are included in state budget documents only as information. Such information mainly contains data on planned and actual indicators, and is necessary, first of all, to increase the accountability of state bodies and transparency of the budget process.
At the same time, it should be noted that when determining the sources of funding for national projects to achieve the strategic goals of economic development, not only public investments from the budget are attracted, but also private investments from extra-budgetary sources of funding, including funds of the population.
Methodology
For national projects, the following main factors have been identified for forming a system of their implementation and financing aimed at ensuring breakthrough results:
– Defining national projects as a portfolio of priority projects;
– Ensuring that expenditures for national projects are separated in the budget classification;
– Transformation of state programs that affect the implementation of national projects (programs) into «pilot programs»;
– Creating a single information resource that ensures the full availability of information about the parameters of national projects, in accordance with the principle of single data entry.
At the stage of developing national projects, proposals that are used in the performance assessment stage should be formulated, and should include:
– Proposals for a system of goals and objectives for the implementation of national projects with a methodology for calculating new proposed indicators, including determining the methodology for calculating indicators, justifying the possibility of using existing forms of federal statistical observation or the need to adjust these forms;
– Proposals for target values of national project indicators, including justification of forecast values of indicators;
– Proposals on the structure of the main activities in the framework of national projects and the expected results of their implementation;
– Proposals for a system of legal regulation measures aimed at achieving the goals of the implementation of national projects;
– Proposals on the amount of financial support for the implementation of national projects, taking into account the maximum amount of financial support from the federal budget for the next financial year and planning period.
The transition from forecast targets for socio-economic development to national projects is a multi-stage process of forming proposals based on forecasts to justify national project options at the macro level, supplemented by proposals from regions containing integrated assessments of municipalities. In connection with these circumstances, possible contradictions are inevitable, but the search for solutions should be aimed at achieving agreed measures, decisions that indicate the relationship between the social and economic development targets and results of national projects.
The system of the implementation of national projects and the subsequent evaluation of their effectiveness includes the following stages at the macro level (Fig.1).
The main priorities for the development of public finance in the implementation of national projects on the principles of project management are:
– Digitalization of tax administration and integration of all data sources into a single information space with subsequent automation of its analysis based on modern technologies for processing large data sets;
– Strategic prioritization of financing national projects (in the proportion of 95:5 – federal and regional budgets) that contribute to the transition of the economy to a qualitatively different pace of development and significantly improve the quality of life of the population;
– Introduction of the «golden rule», according to which the expansion of the economy’s potential and the financing of capital investments are carried out at the expense of a moderate increase in government borrowing based on the principles of long-term sustainability and balance of the country’s budget;
– Reorientation and prioritization of targeted inter-budget transfers in accordance with a differentiated approach to areas and measures of state support for different types of territories, taking into account the economic specialization of the Russian regions, the identified growth points and infrastructure constraints;
– Setting targets for federal projects in the context of Russian regions, which will be reflected in agreements on providing financial support to regional budgets.

Fig. 1: Stages of implementation and evaluation of the effectiveness of national projects
(source: compiled by the authors)
The implementation of results-based management principles at the regional level increasing the efficiency of public finances, and introducing modern budget technologies and tools into the budget process (starting with the development of revenue potential and ending with public debt management) have also become priorities for the socio-economic development of Russian regions. National projects should become a simple and effective tool for organizing both project and process activities of public administration bodies, reflecting the relationship between the resources spent and the results obtained. The achievement of the established values of national projects indicators at the regional level will be taken into account when compiling industry ratings of their performance, and in some cases – when evaluating the activities of governors and when financially encouraging regions through grants.
The involvement of regional public authorities in the implementation of national projects in the process of implementing the program principles of budgeting in the regions led to the formation of the following trends in the development of regional finance:
– Implementation of budgeting in budget practice, which contributes to the coordination of strategic and tactical goals for the implementation of national projects;
– Development of tools for improving the efficiency of budget expenditures by improving the quality of public services and completing the process of developing national projects for the balanced socio-economic development and improving the quality of life of citizens of the country;
– The main guidelines of national projects that have become tools for improving the quality of public finance management are the development of the social sphere, implementation of infrastructure projects, innovative development and modernizationof the economy;
– State programs have an active impact on the economic development of certain territories (Crimea, the far East, Kaliningrad, the North Caucasus) and focus on financial support for projects aimed at solving systemic problems in these regions;
– Improving the efficiency of public investment and procurement, and improving internal financial control and audit procedures.
Statistics and Data Analysis
In 2019-2024, it is planned to allocate more than 25.7 trillion rubles for national projects, of which 29.1% are non-budgetary sources; 51% – means of the federal budget of the Russian Federation and about 20% – means of regional budgets and state extra-budgetary funds.
National projects are financed on the basis of a decree of the Government of the Russian Federation. Average levels of co-financing for subsidies in the context of national projects, despite the threshold value of 95: 5, where 95% of co-financing is provided from the Federal budget, and 5% from regional and local budgets.
In fact, this minimum ratio is much lower and varies from 60: 40 to 82: 18 depending on the industry specifics of the national project (Fig.2).
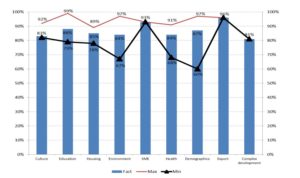
Fig. 2: Average levels of co-financing for subsidies in the context of national projects
The main task of the national project financing system in the country is to develop new schemes and mechanisms for financing national projects that can optimally combine different conditions and sources of financing, as well as attract significant resources to improve the quality and level of the socio-economic development and life in the country on the principles of public-private partnership and initiative budgeting.
Test of Hypotheses
A systematic approach to the consideration of national projects dictates the need to analyze the economic processes that determine their implementation. In this regard, the assessment of the macroeconomic effect of the implementation of national projects is carried out in close relationship with the indicators of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation and the structure of GDP. The methodology for assessing the macroeconomic effect of national projects is based on the methodology for calculating GDP by expenditure method. For this purpose, as part of the assessment of the macroeconomic effect of the implementation of national projects, a general assessment and classification of Federal budget expenditures by economic factors that form the macroeconomic effects of supply and demand in the economy is carried out. The factors that determine the expenditure items of the GDP form the demand in the economy (expenditure on final consumption, investment in fixed capital, government expenditure and net exports). In General, from the point of view of the elements of GDP use, these expenditures mainly form the final consumption of households and public institutions. At the same time, a significant share of expenditures, according to the provisions of the national accounting system, can be classified as investment, and will contribute to the growth of demand for investment goods and services and the accumulation of fixed capital in the economy.
Results
- The process of forming an integrated system of state and municipal finance management in 2019 in Russia at all levels of the state budget system has not yet been completed. A serious budget reform has been carried out, which has made it possible to build a budget process and link the achievement of efficiency between strategic goals, priority tasks of social and economic development in Russia and state programs, as well as national and federal projects. National projects in the system of state and municipal finance have become a key mechanism for linking strategic and budget planning and increasing budget transparency at all levels of the country’s budget system.
- The program budget and its tools are the main mechanism for increasing the socio-economic efficiency of state expenditures. Since 2014, the main tool for improving the efficiency of federal budget expenditures has been the use of a program-targeted method for managing budget resources within the framework of state programs, which ensures their concentration on priority areas of socio-economic development.
- The use of software tools makes it possible to increase the flexibility of budget resources management in achieving strategic goals of economic development, helps to minimize costs and improve the efficiency of providing all types of budget services. In the future, national projects should become a simple and effective tool for organizing both project and process activities of state government, reflecting the relationship between the resources spent and the results obtained within the framework of national projects.
- Trends in the public finance in Russia include increasing the independence of the executive authorities of the Russian regions, reducing the dependence of the consolidated budgets of the Russian regions on financial assistance from the federal budget of the Russian Federation, developing program-oriented methods and improving the quality of public finance management.
- The specifics of implementing national projects require the creation of a quality standard for public services. National projects should address issues aimed at improving the quality of life, improving the living environment, ensuring equal opportunities for education, medical care and health restoration, developing social activities and protecting socially vulnerable groups. At the same time, personnel issues should be resolved in terms of creating comfortable living conditions for the population, including transportation accessibility, development of telecommunications, engineering and social infrastructure, as well as the preservation and improvement of the environment, and cultural and historical landscape of the territories. All this will help improve the quality of life of the population and ensure the inclusion of the population in civil society.
- However, there is still a number of unresolved issues, such as the inability to fully select all budgeted funds for national projects at the federal level. At the regional level, when financing expenditure obligations in the proportion of 95: 5 and its deviations (Fig. 2), there is often not enough money for the implementation of activities of national projects due to the lack of new project mechanisms and often the lack of funds from municipalities for the development of design and estimate documentation, the conclusion of state expertise bodies for capital construction projects.
- The implementation of national projects in Russia is carried out on the basis of implementation plans and detailed schedules for their implementation. For planning and forecasting socio-economic performance indicators of national projects, it is carried out on key points, which also include an annual report on the progress of the implementation and evaluation of the effectiveness of national projects, a report of the responsible executive on the progress of the implementation and a consolidated annual report.
- According to the monitoring results of, the implementation of national projects for 2019 in Russia was relatively effective – not all national projects have a high indicator of the control events that occurred, in addition, there is no opportunity to assess the effectiveness of spending the total amount of funding for all national projects.
- The macroeconomic performance of national programs in the medium term is determined by the volume and dynamics of investment expenditures in the structure of their financing, which form a contribution to the operating flow. The total contribution to the use of GDP in 2019 is estimated at 25.7 trillion rubles (including 5.7 trillion rubles –in human capital, 9.9 trillion rubles – in creating a comfortable living environment and 10.1 trillion rubles in creating conditions for the economic growth in the country), which is approximately 30% of the GDP. According to the estimates, the financing of national projects made a positive and neutral contribution to the GDP growth rate.
- The positive contribution from the increase in financing national projects is offset by the negative impact of their inflationary depreciation. At the same time, the implementation of national projects does not practically lead to additional inflationary pressure, even contributes to a certain slowdown in inflation. The analysis of expenditures financed under national programs by component elements allowed to structure the types of effects depending on the characteristics of the GDP structure – short-term (from the aggregate demand side), medium-term (from the supply side) and long-term (increasing factor productivity) macroeconomic effects.
Discussion of Findings
In international practice, the assessment of the macro-effect of the implementation of program-targeted planning in the budget process was as follows:
- a) An analysis of the structural elements of each of the projects as part of in-depth public administration reforms (Great Britain, Australia, New Zealand);
- b) Within the framework of separate programs for partial modernization of the public administration system that do not affect its fundamental foundations (USA, Canada, Ireland, the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden, France);
- c) Within the constraints of the initiatives to improve the system of public finance management (Norway, Germany, Switzerland).
Each of the described methods involves the use of a final tool or driver for regulating the impact on the national project management system. As indicated in the study, in order to increase macro-efficiency from the implementation of national project activities, it is necessary to activate new growth drivers.Any of the state approaches determines the analysis of expenditures financed within the framework of national projects by component elements and types of effects, depending on the characteristics of the GDP structure:short-term effect-formed from the aggregate demand in the economy (wages, interest expenses, depreciation, profit margin); medium-term effect-formed from the supply side (investments in fixed assets, net exports, expenditures of state administration bodies); the long-term effect is formed by the drivers of the economic growth (investment, new jobs, labor productivity).
These findings are supported by results of current studies.
Recommendations
The study recommends the following:
- a) Based on the results of the evaluation structural elements of national projects, state and regional authorities should formulate consolidated proposals for:
– A system of goals and objectives for the implementation of national projects with a methodology for calculating new proposed indicators, including determining the methodology for collecting statistical data and calculating indicators, as well as searching for alternative sources of statistics;
– Target values of indicators of national projects, including justification of forecast values of indicators;
– Structure of the main activities of national projects and their expected results of implementation;
– A system of legal regulation measures aimed at achieving the goals of implementing national projects;
– The amount of financial support for the implementation of national projects, taking into account the maximum amount of financial support from the federal budget in accordance with the federal law on the federal budget for the next financial year and planning period.
- b) To increase the macro-efficiency of the implementation of national project activities, it is necessary to activate such growth drivers:
– In the short-term as creating new jobs and increasing the level of remuneration of the population,
– In the medium-term – attracting investment,
– In the long-term – increasing the innovation of infrastructure, social sphere and industry in the country.
In the future, national projects should become a simple and effective instrument for organizing both project and process activities of public authorities, reflecting the relationship between the resources spent and the results obtained.
Conclusion
National projects are a key mechanism for strategic and budget planning and increasing budget transparency at all levels of the country’s budget system. The process of forming an integrated system of national project management is based on a program-oriented approach and requires the creation of a quality standard for public services to improve the level and quality of life of Russian citizens. As a result of the implementation of national projects in 2019, a number of unresolved issues were identified, such as the inability to fully select all budgeted funds for national projects at the federal level, although at the regional level there is often not enough money for the implementation of activities due to the lack of new project mechanisms and lack of funds at the local level. According to the conducted estimates, the financing of national projects has made a positive and neutral contribution to the GDP growth rate, but not all national projects have a high indicator of the control events that occurred, in addition, it is not possible to assess the effectiveness of spending the total amount of funding for all national projects. In order to increase the macro-efficiency of implementing national project activities, it is necessary to activate such growth drivers in the short-term as creating new jobs, increasing the level of remuneration for the population, attracting investment in the medium-term, and increasing the innovation of infrastructure facilities in the long-term.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
References
- Blennerhassett S. and Farrant W., Jones Ja. (1989),’Support for community health projects in the UK: a role for the national health service’,Health Promotion International, 4 (3), 199.
- Ermilova M. andFinogenova Y. (2017),’The impact of macroeconomic factors and economic cycles on the cost of housing’,International Journal of Ecological Economics and Statistics, 38 (2), 68-77.
- Kosov M.E., Akhmadeev R.G., Bykanova O.A., Osipov V.S., Ekimova K.V. andFrumina S.V. (2016),’Economic practicability substantiation of financial instrument choice’,Journal of Applied Economic Sciences, 11 (8), 1613-1623.
- Kutsenko E. andEferin Y. (2019),’“Whirlpools” and “Safe Harbors” in the Dynamics of Industrial Specialization in Russian Regions’,Foresight and STI Governance, 13 (3), 24-40.
- Kutsenko E., Islankina E. andAbashkin V. (2017),’The evolution of cluster initiatives in Russia: the impacts of policy, life-time, proximity and innovative environment’,Foresight, 19 (2), 87-120.
- Leto Ya.A. (2017),’Crowdfunding or national funding of socio-cultural projects’,Economics, 2 (23), 20-27.
- Newman P. and Thornley A. (1998),’Urban planning in Europe, international competition, national systems, and planning projects’,Environment and Planning A. 30 (3), 559-560.
- Slepov V.A., Burlachkov V.K., Danko T.P., Kosov M.E., Volkov I.I., Ivolgina N.V. andSekerin V.D. (2017),’Model for integrating monetary and fiscal policies to stimulate economic growth and sustainable debt dynamics’,European Research Studies Journal, 20 (4), 457-470.
- Slepov V.A., Kosov M.E., ChalovaA.Yu., Gromova E.I. andVoronkova E.K. (2019),’Integration of the financial market sectors: factors, risks and management approaches’,International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 10 (2), 1243-1250.
- Kitova O.V., Kolmakov I.B., Dyakonova L.P., Grishina O.A., Danko T.P. andSekerin V.D. (2016),’Hybrid intelligent system of forecasting of the socio-economic development of the country’,International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 14 (9), 5755-5766.
- Ragulina Y.V., Musayev R.R. andElesina M.V. (2013),’The analysis of foreign practice of territory development on the basis of the implementation of national projects’,Science and Technology, 1, 157-166.
- Simon M.J., Chesner W.H. andEighmy T.T. (2000),’National research projects on recycling in highway construction’,Public Roads, 64 (1), 2-10.
- Shugrue M.F. (1967),’National English projects and curriculum change’,NASSP Bulletin, 51 (318), 92-100.
- Johns E.B. (1968),’Two national projects in health education’,NASSP Bulletin, 52 (326), 70-80.
- Jung Y.J., Stenstrom M.K., Jung D.I., Kim L.H. and Min K.S. (2008),’National pilot projects for management of diffuse pollution in Korea’,Desalination, 226 (1-3), 97-105




