Introduction
In the digitally challenged world, strategic marketing planning demands in-depth awareness of customer needs, preferences, and experiences. Moreover, it considers the ability to respond quickly to acquired customer information. The capability to make real-time and data-driven decisions has made AI a tactical marketing approach. However, the integration of AI marketing into strategic marketing campaigns must be cautious due to being in the early stages of assimilation.
Artificial intelligence marketing demonstrates a practical and comprehensive way to harness the power of data-driven marketing strategies and achieve the utmost success for the companies. Moreover, in practice, strategic thinking circulates 4Ps, and 5Cs and tends to disregard the digital window to perform.
Marketing teams are embracing intelligent solutions to nurture a compelling customer experience. Effective Al-powered solutions provide marketers with significantly powerful platforms to manage the massive amount of data collected. In addition, those technologies increase marketers’ understanding of target audiences. Besides, those results enable drive conversations between companies and various target audiences. Consequently, the principles of AI marketing are focused not only on return on investment but on sustainable growth and development.
AI possesses a crucial role in assisting marketers in connecting with prospective customers. Moreover, AI marketing helps bridge the gap between customer data and the actionable next steps. Notably, providing an in-depth analysis of audiences may impact marketing efforts. Hence, a key outcome is assessing customer profiles to best customize messages at the right time, with less human involvement and maximum efficiency.
The paper aimed to illustrate existing circumstances of artificial intelligence in marketing practices, hence, exploring the applicability of AI marketing for creating data-driven marketing strategies. The secondary data for the analysis are obtained from various annual reports, scientific journals, etc. An extensive literature review highlights four main themes: analyzing and understanding customer satisfaction, employing AI to improve positioning, applying AI for accurate decision-making, and employing AI for sales, cost, and risk reductions. Three hundred sixty-seven marketing practitioners with 22 different marketing professions, representing 11 countries from 18 different industries, mainly from the Baltic and Caucasus regions, voluntarily voiced their opinions within 1-year of data collection.
This research synthesizes artificial intelligence drivers, barriers, and outcomes in marketing and highlights critical areas for future focus. Besides, the analysis highlights the benefits of using AI marketing and its applicability in data-driven marketing strategies. Furthermore, it shows a positive relationship with utilizing AI in long-term strategic marketing planning. Besides, it provides context for future research in AI marketing. Lastly, the proposal is developed for the practical application of AI marketing in data-driven strategic marketing.
The following sections present a literature review, research methodology, findings and results, and conclusions.
Literature Review
The marketing world is going through a radical transformation with machine learning and artificial intelligence (Syam & Kaul, 2021). Besides, the world we live in is changing at an accelerated pace, driven by technological development. Moreover, the change’s speed, depth, and scale revolutionize the entire sector of sustainable marketing and its applicability in market strategy (Rudawska, 2018).
Marketing is still about reaching consumers effectively, informing them, persuading them, motivating them, and ideally bringing them back for more (Pradeep et al., 2019). Furthermore, adjusting marketing strategies to attract consumers requires information about the factors that affect consumption and the ability to decipher and transform them into specific marketing strategies (Theodoridis, Sarmaniotis, & Stalidis, 2019).
Rindfleisch & Alan (2019) argued that now, in the digital age, computers, smartphones, and social media link individuals worldwide, providing endless potential for connecting or disconnecting. Thus, according to Wilson (2019), the wealth of new data poses a substantial threat and untapped opportunity for individuals, practitioners, and businesses alike when it comes to ideating and producing effective business and marketing content, as well as keeping in touch with growing online and offline competition.
Dumitriu & Popescu (2020) argued that marketing had reached a point in its evolution where adapting to digital trends is imperative. However, according to (Soni, 2020; Chen et al.,2021), although it seems to be a push for marketers, all automated applications and systems based on AI only diminish the complexity of the classic targeting and customization process.
The new form of intelligence is different from our own, and it perceives the world through the prism of Big Data. It has its logic, it seems to be from elsewhere, and this elsewhere is the primary development center of key digital players (Latrate, 2018). Hence, Kumar et al. (2019) enlightened that artificial intelligence is aiding an approach to creating, communicating, and delivering personalized offerings to customers.
The artificial intelligence market is currently flourishing (Latrate, 2018). Thinking AI is excellent at recognizing relationships and regularities in data (Huang & Rust, 2021). Besides, practitioners are trying to determine the best fit for AI solutions for their marketing functions (Verma, Sharma, Deb, & Maitra, 2021). AI practices can improve by seeing and synthesizing consumers’ non-conscious needs and wants to lessen uncertainty (Pradeep, Appel, & Sthanunathan, 2019). Furthermore, creating new and effective AI algorithms requires top competent talent. Currently, the demand overweights the supply of qualified professionals. AI needs to be trained in a structured and unstructured way (Wilson, 2019). Hence, artificial intelligence finds applications in a different context in today’s business scenario.
Today, the emerging and critical issue for marketers is not whether to use AI to address these challenges and many others but which AI technologies and methodologies to use (Pradeep et al., 2019). Moreover, incorporating digital strategy into firm strategy is a core competency in producing value and essential positioning (Zahay, 2020).
Artificial intelligence has knocked on the doors of business organizations as an imperative activity (Dhamija & Bag, 2020). Besides, with the development of technology, artificial intelligence is gaining increasing attention from both the scientific and the public (Arsenijevic & Jovic, 2019).
De Bruyn et al. (2020) argued that most AI applications in the business area refer to the use of deep artificial neural networks to solve complex predictive tasks that were deemed unsolvable less than a decade ago. Moreover, according to Vlacic et al. (2021), an increasing amount of research on AI in marketing has shown that AI can mimic humans and perform activities in an “intelligent” manner. Consequently, AI is becoming increasingly important in marketing.
Today, it is impossible to talk about customer relations without mentioning the devices that allow us to connect to our digital world anywhere at any time. Customers engage in creativity and in particular, invention and innovation (Sudharshan, 2020, p. 27). Besides, according to Jelassi & Martinez-Lopez (2020), affecting all aspects of the business requires depth analysis. Huang & Rust (2021) supported claiming that AI can be used for data collection, marketing analysis, and feeling AI for customer understanding.
Artificial intelligence-based application is emerging in a broad range of expert domains (Wirth, 2018). Besides, Ivanov & Webster (2019) indicated that AI is currently applied in various fields for speech recognition in digital assistants, chatbots, social media websites, etc. Moreover, chatbot makes it possible to scale and automate the lead qualification process (Cancel & Gerhardt, 2019). Moreover, any marketing functions and activities that benefit from personalized outcomes should consider AI (Huang & Rust, 2021).
People interact with some form of AI in daily activities (Feng et al.,2020; Mustak et al., 2021; Paschen & Kitzmann, 2019). Therefore, AI gives marketers a richer user understanding, making them more innovative and effective (Olson & Levy, 2018). Moreover, according to Davenport et al. (2020), AI can sustainably change both marketing strategies and customer behavior.
To conclude, Pitt et al. (2021) argued that Artificial intelligence is a killer app with specific marketing applications. Besides, according to Verma et al. (2021), AI is the latest technological disrupter and holds immense marketing transformation potential. The imperative is clear, marketing professionals today must integrate AI into their marketing strategies if they expect to keep up with, much less bear, the competition (Pradeep et al., 2019).
Research Methodology
The author employed a quantitative research method with a survey methodology. The research evidence was based on data from 367 marketing specialists from 22 different marketing professions, 11 countries, and 18 industries. Analyzing information from different industries and countries was essential because AI in marketing has different requirements that may affect how businesses approach the purpose of AI in marketing strategies.
The approach of this research was to illustrate the existing circumstances of artificial intelligence in marketing processes, hence, investigating the applicability of AI marketing for creating data-driven marketing strategies. Artificial intelligence offers various components that allow marketing specialists to simplify marketing objectives and reach targeted goals.
To address the research question and investigate the applicability of AI marketing for creating data-driven marketing strategies, the author applied a two-step strategy. First, a systematic literature review was conducted to identify the knowledge gap and create a research ground. To verify the authenticity of the data analysis, NVivo12 software was used. Consequently, after reviewing around 75 scientific journals, annual reports, professional publications, and so and reports, twenty-nine were worthwhile for this paper. NVivo12 assisted in identifying four main themes: examining insight on customer satisfaction, employing AI to improve positioning, applying AI for accurate decision-making, and employing AI for sales, cost, and risk reductions.
Second, based on the analyzed literature and themes, a survey study was created using QuestionPro software. Questions were designed purposefully to obtain detailed insights from marketing practitioners. Respondents had to reflect on to what extent certain statements apply to their job, company, or business. This approach enabled us to obtain the most current information on the usage of AI in marketing for data-driven strategic planning. Pre-testing was conducted to formalize the statistical significance and relationships between variables. Afterward, a survey was sent to the target population.
Research Findings and Results
The research was conducted for 1-year between February 1st, 2021, to January 11th, 2022. During this time, around 1,500 marketing practitioners were approached to participate in the research, from which 547 viewed the survey. Consequently, from 547, only 367 willingly filled the survey through QuestionPro. Others, for unknown reasons, opted not to continue with the questionnaire. Hence, it was a massive sample size to examine data.
The represented sample was diverse. The male to female ratio was 40.1% against 52.9%, while 4.6% chose “prefer not” and 2.5% other. Moreover, the majority of respondents represented age groups: “18-24” with 23.7%, “25-34” with 33%, and “35-44” with 22.1%. Moreover, respondents were represented from 11 countries which later was broken into four sub-groups: Baltic, Caucasus, Other (EU- Turkey, Belgium, the Netherlands, Greece, Spain, and Slovakia), and Other (USA).
Figure 1 and Figure 2 below highlight marketing professions and industries represented in this population sample. The “travel” industry represented many marketing practitioners with 31.1%, followed by “technology” with 11.4%, and “education” with 10.4%. Least represented were “logistics” with 3.3 % and “telecommunications” with 1.6%. Besides, the top specialist was from a “search engine optimization” with 13.1%, followed by “social media manager” with 11.2%, and “marketing specialist” with 10.1%. The least popular occupation in the sample was “communications director” with 0.8%, “media buyer” with 1.1%, and “telemarketing” with 1.4%.
For the research, it was significant to have such a diverse workforce and industry representation with practical experience in the field of marketing. 25.1% of respondents have been in the field between “2 to 5 years”, followed by “1 to 2 years” with 18.5%. “5 to 7 years” and “more than 10 years” had almost equal representation with 15.3%. Additionally, 10.6% represented experience between “8 to 10 years”. The least experienced was 6.5%, represented by “less than 6 months of experience”. These data highlighted how companies in different countries apply artificial intelligence in data-driven decision-making or not. It should be noted that every industry has different methodologies and procedures concerning AI practices.
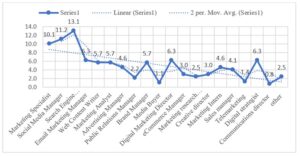
Fig 1. Marketing Professions
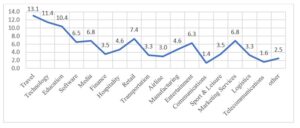
Fig 2. Industries of Employment of marketing practitioners
Figure 3 illustrates four different questions that were asked to the marketing practitioners regarding identifying the value of data-driven solutions and AI. The first question was to what extent AI marketing is relevant in today’s strategic marketing planning for creating data-driven marketing strategies. As illustrated in figure 3, most practitioners “quite” believed that it is essential. On the other hand, 18.5% of respondents underlined “Not at all.” It supports the statement that integrating AI marketing into strategic marketing campaigns must be cautious due to being in the early stages of development.
Many marketing professionals might not be eager and excited about using various algorithms to develop strategies. Due to this, participants were asked to respond to what extent were data-driven marketing strategies important in business? Figure 3 highlights the differences. 15.8% and 16.1% selected “slightly” and “Not at all” compared to “extremely” with 18.3%. However, 33% still believe it is “Quite” necessary versus 16.9% selecting “Somewhat.”
Furthermore, participants were asked to what extent AI disrupted the marketing environment. Figure 3 illustrates an exciting trend. The feedback from participants is almost the same, just slight differences. For example, the range between maximum and minimum is 16.6% to 24.8%. 16.6% falls on the opinion “Quite” disrupted while the maximum falls on the opinion “extremely.” 17.7% identified as “Not at all,” while 19.3% “slightly.” Quite many respondents selected “somewhat.”
Lastly, in this context, it was essential to see to what extent AI marketing was aligned with respondents’ current marketing strategies. Nevertheless, figure 3 demonstrated that 36.5% “slightly” use AI marketing in current marketing strategies, which is not surprising due to the complexity, and many companies do not have software to track data. Moreover, approximately 34% use AI marketing which was a favorable outcome showing that some companies still have the capabilities to use expensive software.
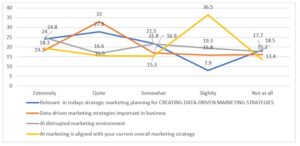
Fig 3. Relevance of creating data-driven marketing strategies
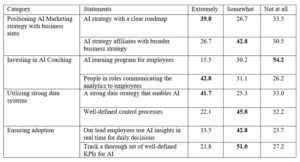
The next group of questions explored the in-depth applicability of AI marketing within the companies of research participants. Table 1 illustrates four different categories, each with two different statements about AI and data strategies. Respondents had to reflect on what extent they agree or disagree with statements and their applicability in their own companies. Values “5” and “4” were classified under “Extremely,” value “3” as “somewhat,” and Values “2” and “1” as “Not at all.”
Aligning an AI marketing strategy with business aims is the primary objective of any company. Hence, the author inquired to what extent it was applied in the respondents’ companies. The first statement was “we have an AI strategy with a clear roadmap,” to which respondents elected “extremely” with 39.8%. On the contrary, “the AI strategy affiliates with broader business strategy” respondents were not quite sure and selected “Somewhat.” Nevertheless, it showed on a certain level that companies in various industries are applying AI in marketing strategies, and more importantly, it is somewhat affiliated with the overall business aims.
The next category was investing in AI coaching. 54.2% of respondents selected “Not at all” on the statement “AI learning program for employees.” In contrast, “People in roles communicating the analytics to employees” was 42.8%. It was an essential element to explore due to the applicability of AI marketing and how the company itself deals with the technologically challenged world. Furthermore, in the following category, whether the company applies strong data practices showed a positive relationship with 41.7%. However, it does not mean that AI is strongly supported. 45.8% identified that the company has “somewhat” well-defined control processes for critical data-related decisions. In this context, as technologies are getting modified, the author was curious to explore whether companies have a standard AI tool and how they deal with how frequently AI approaches need to be updated.
Lastly, the following category was the enduring implementation of AI insights in daily decision-making. 42.8% of respondents identified that “Somewhat” “lead employees use real-time data to make daily marketing decisions.” Furthermore, 51% of respondents indicated that their companies “Somewhat” use a comprehensive set of well-defined KPIs for AI. Even though it was not a majority, it still indicates a positive relationship between AI in marketing and data-driven decision-making.
Table 1. AI and data strategies in marketing practitioners’ companies
The research defined the benefits of AI marketing for data-driven marketing strategies. Throughout analyzing three open-end questions, the top five benefits were specified as “making better decisions,” “pursuing new markets,” “freeing up workers for more creative automating tasks,” and “enhancing the features and functions of the products,” and “optimizing internal marketing operations.” These benefits clearly can be placed within the categories in Table 1, confirming the significance of the applicability of AI marketing.
To continue, respondents reflected on what was their expectations of AI marketing in today’s digital environment. Respondents were given seven options to select only one. 18.8% selected “help to identify prospective customers,” 21.8% selected “provide more detailed analysis of campaigns,” and 6.8% selected “identify specific account opportunities.” Moreover, 15.3% selected “making marketing planning easier,” 21.3% selected “improving marketing effectiveness in driving revenue,” and 9.3% selected “not quite sure if I understand the relevance of AI marketing.” Moreover, 6.8% selected “other” but did not specify. This information reflects the role of AI marketing in data-driven decision-making. However, it should be noted that 9.3% of respondents not understanding the essence of AI marketing is significant. One more time indicating the complexity of AI and data-driven approaches. Furthermore, from a personal point of view, 21.5% of respondents indicated that AI marketing would “facilitate better-decision making,” followed by “save money” 24.3%, “Have more fun” 17.2%, and “having easier access to the data” with 15%.
To address the research question, respondents were asked to indicate for what purposes AI marketing was applicable to data-driven marketing strategies. Respondents were given nine options to choose from. Figure 4 illustrates the feedback obtained. The data are broken down according to the regions. It was critical to see that the Baltic and Caucasus regions had an almost similar trend towards applicability compared to the EU and the US. It should be underlined that there were respondents who indicated that they “do not know” whether it is applicable or not, which underlines feedback obtained in table 1.
Accordingly, it should be noted that creative content creation, email marketing, and automated campaigns were the most significant; however, the author believes that optimization and digital management also should be considered as the top reasonings. Furthermore, data analysis was also recognized by the respondents, especially in the Baltic and Caucasus regions’ respondents.
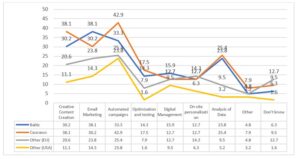
Fig 4. The purpose of AI Marketing
Conclusion
Enormous transformation is happening in the marketing industry derived from the development of digital technologies. More and more companies are utilizing artificial intelligence in their strategies; however, it is not fully embraced due to complexity or lack of resources.
Through systematic literature review, analyzing various high quality scientific and professional journals and annual reports, four main themes: examining insight on customer satisfaction, employing AI to improve positioning, applying AI for accurate decision-making, and employing AI for sales, cost, and risk reductions, were identified and carefully studied through primary research.
A quantitative survey was developed based on the identified themes to explore the applicability of AI marketing in data-driven marketing strategies. For that purpose, 11 countries, 18 industries, and 22 marketing professions were represented across 367 participants. Obtained data demonstrated key elements through experience and professions held by the respondents. Moreover, they have reflected based on current situations in their respected companies, hence, obtaining quality data.
The main research question of whether AI marketing applied to data-driven marketing strategies was positively answered throughout the demonstrated data above. However, it must be emphasized that results are based on numerical numbers; however, further empirical work is needed.
The research synthesized artificial intelligence drivers, barriers, and outcomes in marketing and highlighted critical areas for future focus. Besides, the analysis emphasized the benefits of using AI marketing and its applicability in data-driven marketing strategies. Outcomes showed a positive relationship with utilizing AI in long-term strategic marketing planning. Besides, it offers a framework for future work and allows for more research in AI marketing.
The research offers practical guidance to the companies or inspires leaders in marketing to conduct more research on artificial intelligence as the usage of AI is long-term and will wholly transform industries.
References
- Arsenijevic, U., and Jovic, M. (2019). Artificial Intelligence Marketing: Chatbots. IEEE.
- Cancel, D., and Gerhardt, D. (2019). Conversational Marketing : How the World’s Fastest Growing Companies Use Chatbots to Generate Leads 24/7/365 (and How You Can Too). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
- Chen, L., Jiang, M., Jua, F., and Liu, G. (2021). Artificial intelligence adoption in business-to-business marketing: toward a conceptual framework. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing.
- Davenport, T., Guha, A., Grewal, D., and Bressgott, T. (2020). How artificial intelligence will change the future of marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48, 24-42.
- De Bruyn, A., Viswanathan, V., Shan Beh, Y., Jurgen, B., and von Wangenheim, F. (2020). Artificial Intelligence and Marketing: Pitfalls and Opportunities. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 91-105.
- Dhamija, P., and Bag, S. (2020). Role of Artificial Intelligence in operations enviornemnt; a review and bibliometric analysis. In A. Douglas, P. Found, & A. Chiarini, Industry 4. 0 Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 32, pp. 869-896). Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Dumitriu, D., and Popescu, M. (2020). Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Digital Marketing. Procedia Manufacturing, 630-636.
- Feng, C. M., Park, A., and Pitt, L. (2020). Artificial intelligence in marketing: A bibliographic perspective. Australasian Marketing Journal.
- Huang, M., and Rust, R. T. (2021). A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 49, 30-50.
- Ivanov, S., and Webster, C. (2019). Robots, Artificial Intelligence and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Jelassi, T., and Martinez-Lopez, F. J. (2020). Strategies for E-Business : Concepts and Cases on Value Creation and Digital Business Transformation (Vol. 4). Springer International Publishing AG.
- Kumar, V., Rajan, B., and Venkatesan, R. (2019). Understanding the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Engagement Marketing. California Management Review.
- Latrate, F. (2018). Artificial Intelligence and Big Data : The Birth of a New Intelligence. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
- Mustak, M., Salminen, J., Ple, L., and Wirtz, J. (2021). Artificial intelligence in marketing: Topic modeling, scientometric analysis, and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 389-404.
- Olson, C., and Levy, J. (2018). Transforming marketing with artificial intelligence. Applied Marketing Analytics, 291-297.
- Paschen, J., and Kitzmann, J. (2019). Artificial intelligence (AI) and its implications for market knowledge in B2B marketing. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing.
- Pitt, C., Paschen, J., and Kietzmann, J. (2021). Artificial Intelligence, Marketing, and the History of Technology: Kranzberg’s Laws as a Conceptual Lens. Australasian Marketing Journal .
- Pradeep, A. K., Appel, A., and Sthanunathan, S. (2019). AI for Marketing and Product Innovation : Powerful New Tools for Predicting Trends, Connecting with Customers, and Closing Sales. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
- Rindfleisch, A., and Alan, M. (2019). Marketing in a Digital World (Vol. 17). Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Rudawska, E. (2018). The Sustainable Marketing Concept in European SMEs : Insights from the Food and Drink Industry. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Soni, V. (2020). Emerging Roles of Artificial Intelligence in Ecommerce. International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development, 4(3), 223-225.
- Sudharshan, D. (2020). Marketing in Customer Technology Environments : Prospective Customers and Magical Worlds. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Syam, N., and Kaul, R. (2021). Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Marketing and Sales : Essential Reference for Practitioners and Data Scientists. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Theodoridis, C., Sarmaniotis, C., and Stalidis, G. (2019). Marketing Intelligence in Retail and Distribution Management (Vol. 9). Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Verma, S., Sharma, R., Deb, S., and Maitra, D. (2021). Artificial intelligence in marketing: Systematic review and future research direction. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(1).
- Vlacic, B., Corbo, L., Costa e Silva, S., and Dabic, M. (2021). The evolving role of artificial intelligence in marketing: A review and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 128, 187-203.
- Wilson, L. (2019). Data-Driven Marketing Content : A Practical Guide. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Wirth, N. (2018). Hello marketing, what can artificial intelligence help you with? International Journal of Market Research
- Zahay, D. (2020). Digital Marketing Management, Second Edition : A Handbook for the Current (or Future) CEO (Vol. 2). New York: Business Expert Press.







