Introduction
Leadership creates a strong impact on the attitude of the employees working in the organization. In the present context, however, the roles of leaders have changed to a great extent. The success of an organization relies on the leadership styles being followed by the leaders of the organization. For any organization to be successful, leadership and employee job satisfaction play an important role (Ramos, 2014). As effective leaders provide proper direction and lead to followers for achieving the desired goals; the employees having high job satisfaction become able to perform effectively and pursue organizational interests (Sarwar, et al., 2015). Various researchers have examined the association between the two aspects and agreed that leadership creates a significant impact on job satisfaction among the employees (Valentine, et al., 2011).
There are various types of leadership styles being used by the leaders in accordance with the organizational environment to deal with the employees in accordance. The present study intends to identify the relationship association leadership styles and employee job satisfaction.
Theoretical Framework and Hypothesis
Leadership Styles
According to Northouse (2007), leadership is considered as a practice through which a leader influences a group of people or followers to achieve collective goals. In the present scenario, leaders do not rely on their appropriate authority to influence the followers to perform or follow what has been ordered to them, but they prefer to be interested in collaborating with their subordinates and increase and extend the interest of their subordinates (Northouse, 2015).
The transformational as well as transactional leadership styles that have been presented by Burns, (1978) & Bass (1985) are considered to be highly significant and most widely used in organizations and in leadership studies as well (Bass, 1985). According to Burns (1978), leaders are said to possess transformational leadership traits, when they emphasize upon encouraging their subordinates to escalate the level of their associations, beliefs, morals, insights, and be motivated with the organizational objectives (Burns, 1978).
According to Berson & Avolio (2004), transformational leaders support their subordinates to become productive, innovative as well as compliant to varying organizational environments and make efforts to prevent the probabilities of work related issues (Berson & Avolio, 2004).
On the other hand, transactional leadership style refers to the exchange between the leaders and their subordinates. According to Richter et al. (2016), it is considered as a leader and follower exchange based leadership approach, in which the leader interchanges rewards or punishment with the followers for the performance of tasks, and in response, expect productivity, efforts as well as loyalty from the followers (Richter, et al., 2016). In order to satisfy their self-interests, transactional leaders regulate the strategies to make the followers perform in the way they want. They are perceived to be less engaged, less appealing, during rewards procedure, keep on focusing on the work achieved, mistakes, and avoid interfering in the organizational processes. Due to this reason, it has been observed that a majority of employees prefer transformational leadership instead of transactional leadership (Naidu & Walt, 2005).
Job Satisfaction
As defined by Aziri (2011), job satisfaction is considered as a positive emotional status from the point of view of job or experience in work. It explains that employees develop an attitude towards their jobs considering their behaviors, beliefs and emotions (Aziri, 2011). It has been found that employees are perceived to be satisfied with their jobs, if they consider their jobs to be fulfilling and rewarding. The level of satisfaction among the employees is generally considered as an essential component for organizational success (Javed, et al., 2014).
According to the theory of transformational and transactional leadership, leaders have a great influence on the way their subordinates complete their work (Bektaş, 2017). This influence has the potential to increase the overall job satisfaction of the employees. The job satisfaction can be divided into three major aspects – extrinsic, intrinsic and general job satisfaction. The scales of extrinsic and intrinsic satisfaction scale are obtained from the theory of Herzberg. The intrinsic satisfaction is related to motivators such as job content and working with others. The extrinsic job satisfaction on the other hand is associated with aspects such a company policies, compensation and supervision (Goetz, et al., 2012).
Relationship between Leadership Styles and Job Satisfaction
Bhatti et al. (2012) conducted a research to determine the effect of autocratic and democratic leadership styles on job satisfaction in both public and private schools. After conducting the research, the researchers revealed that the leadership styles create a positive impact on job satisfaction among the employees. It was also revealed by the researchers that public teachers have a high level of job satisfaction instead of private teachers (Bhatti, et al., 2012). The reason behind this was found to be less secured jobs in the private sector instead of public sector. It was found that the leadership styles followed by the public schools make employees feel fearless to discuss issues with their leaders which create a sense of responsibility among them.
Study conducted by Voon, et al. (2011) indicates that transformational leadership style possesses a stronger relationship with job satisfaction, while transactional leadership style possesses a negative relationship with job satisfaction among employees. The research study suggested that transformational leadership should be considered suitable for managing government organizations (Voon, et al., 2011).
The study conducted by Saleem (2015) aimed to examine the effect of leadership styles on job satisfaction and understand if supposed organizational politics had an intermediating role or not. To achieve the purpose, the researcher utilized descriptive research design and conducted a quantitative research. The researcher selected the sample through non-probability convenience sampling. The findings of the research revealed that transformational leadership have positive influence on job satisfaction while transactional leadership have negative influence on job satisfaction. It was also suggested by the researcher that apparent organizational politics moderately mediate the association between both the leadership styles and job satisfaction (Saleem, 2015).
Based on the theoretical background discussed above, the following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 1: Transformational leadership promotes intrinsic job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
Hypothesis 2: Transformational leadership promotes extrinsic job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
Hypothesis 3: Transformational leadership promotes general job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
Research Methodology
Methodology of the Empirical Research Sample and Procedure
The population of this research included the employees from organizations of Abu Dhabi. The samples for this study are taken from companies that are located in Abu Dhabi. Purposeful sampling is used in this research. In other words, the individuals who were relevant for understanding the phenomenon taken under consideration were selected intentionally for this study. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between different variables in the chosen companies in Abu Dhabi (Khan, 2011).
The participants of the study included full time employees such as workers, managers and the administrative staff. 200 surveys were sent to the individuals selected from these organizations. The response rate of the survey was 60.5 %. As a result a final sample of 121 respondents was obtained. F tests were performed for determining the statistical significance of the regression models of this study.
Measurement
In this study the current version of the MLQ-5X was used for assessing the transactional and transformational leadership. The MLQ -5X was developed in 1997 by Bass and Avolio. The purpose of this particular study was to determine the best prediction of job satisfaction of the employees, therefore, the rater form of MLQ -5X was used.
The assessment of job satisfaction was done with 20 questions derived from short form of MSQ (Weiss & Dawis, 1967). The scales of intrinsic and extrinsic job satisfaction were derived from the Herzberg’s (1966) two-factor theory of job satisfaction.
Results and Findings
H1: Transformational leadership promotes intrinsic job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
Table 1 shows the correlation among transactional, transformational leadership style and intrinsic job satisfaction. There was a significant positive correlation among the transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and intrinsic job satisfaction (p < 0.001). The table 1 also indicates the Pearson correlation between the two leadership styles. The correlation was 0.53 between the independent variables. The two independent variables were retained in the model of multiple regression because the correlation is less than 0.7 (Pallant, 2016)
Table 1: Correlations between Leadership and Intrinsic Job Satisfaction
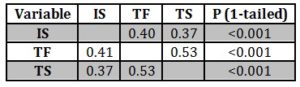
Table 2 indicates that the value of R2 was 0.20 indicating that there is a variance of 20% in the model and the intrinsic job satisfaction.
Table 2 : Model Summary of multiple regression analysis

Table 3: ANOVA for transformational and transactional leadership and job satisfaction
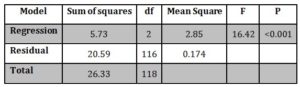
The standardized coefficients were used for determining the variable that contributed most in predicting the dependent variable. The transformational leadership has the strongest contribution in predicting the intrinsic job satisfaction with a β coefficient = 0.30. The β value for transactional leadership was lower (0.23), this indicates that this particular variable contributed less in predicting the intrinsic job satisfaction. Further, the t value was also evaluated for each variable. It was found that the variables (transformational and transactional leadership style) made significant contributions in prediction of the dependent variable as the significance value of the variables were >0.05.
Further, for each variable, the value of t was determined. The significant levels of the two variables of the study were > 0.05. This indicates that the variables (transformational and transactional leadership) have made significant unique contributions in predicting the dependent variable of the study (job satisfaction) as for the transformational leadership
p =0.03 and for transactional leadership style p = 0.018.
H2: Transformational leadership promotes extrinsic job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
The Table given below displays the correlation between transformational and transactional leadership style and extrinsic job satisfaction. Significant positive correlations were found between the transformational and transactional leadership and extrinsic job satisfaction as the (p < 0.001). The Table below also displays the Pearson’s correlation between the two leadership styles. The correlation between variable = 0.53 (less than 0.7), therefore the independent variables were retained.
Table 4: Correlations between Leadership and Intrinsic Job Satisfaction
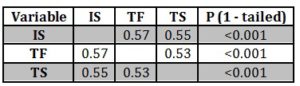
The table given below indicates that the value of R2 = 0.41. This indicates that the there is 41% variance in the model and the extrinsic job satisfaction. The model is significant statistically (F = 42.92, p < 0.001).
Table 5: Model Summary of Multiple Regression Analysis

Table 6: ANOVA for Transformational and Transactional Leadership and Extrinsic Job Satisfaction
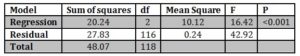
Standardized coefficients were used for determining the contribution of the variables that are included in the model. The transformational leadership has a unique contribution in predicting the extrinsic job satisfaction as the β coefficient = 0.40. The value of β for the transactional leadership was lower (0.34), this indicates that transactional leadership made less unique contribution.
For each variable, the t value was also determined. The significant levels of the two variables of the study were > 0.05. This indicates that the variables (transformational and transactional leadership) have made significant unique contributions in predicting the dependent variable of the study (job satisfaction) as p < 0.001 for the variables.
H3: Transformational leadership promotes general job satisfaction of employees better than transactional leadership.
The table displayed below presents the correlation between transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and general job satisfaction. Positive and significant correlations were found between the transformational and transactional leadership style and extrinsic job satisfaction as the (p < 0.001). The Table below also displays the Pearson’s correlation between the two leadership styles. The correlation between variable = 0.54 (less than 0.7) therefore the independent variables were retained.
Table 7: Correlations between Leadership and Intrinsic Job Satisfaction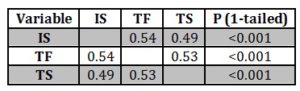
The table given below indicates that the value of R2 = 0.41. This indicates that there is 41% variance in the model and the extrinsic job satisfaction. The model is significant statistically (F = 42.92, p < 0.001).
Table 8: Model Summary of Multiple Regression Analysis
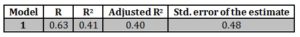
Table 9: ANOVA for Transformational and Transactional Leadership and General Job Satisfaction
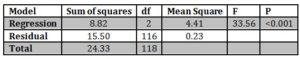
Standardized coefficients were used for determining the contribution of the variables that are included in the model. Transformational leadership has a unique contribution in predicting the extrinsic job satisfaction as the β coefficient = 0.39. The value of β for the transactional leadership was lower (0.29) indicating that transactional leadership made less unique contribution.
For each variable, the t value was also determined. The significant levels of the two variables of the study were > 0.05. This indicates that the variables (transformational and transactional leadership) have made significant unique contributions in predicting the dependent variable of the study (job satisfaction) as p = 0.001 for the transactional leadership and p < 0.001 for transformational leadership.
Discussion
This particular study was conducted so as to explore the relationship between the leadership styles and job satisfaction of employees in the selected organizations of Abu Dhabi. According to the results of Pearson’s correlation the two leadership styles positively and significantly correlated with the intrinsic job satisfaction.
The standardized coefficients β for the transformational and transactional leadership indicated that transformational leadership contributes more in the model rather than the transactional leadership style.
The findings of study indicate that transformational leadership better predicts the intrinsic job satisfaction rather than transactional leadership. The findings of study suggest that the intrinsic job satisfaction of the employee can be increased if the transformational leadership style is used.
The findings of this study are consistent with the findings of past studies. According to Shibru and Darshan (2011) the transformational leadership style is one of the important factors that help in improving the job satisfaction level of the employees. The findings of the study indicated that the transformational leadership style can increase the job satisfaction of the employees (Darshan, 2011).
The conclusions of this study are drawn from the responses obtained from 121 respondents of organizations from the UAE. Therefore, the responses cannot be generalized to the whole population. The findings of this study may help in understanding the perception of the employees.
Conclusions, Limitations, Further Research and Practical Implications
This particular study has provided evidences regarding the association between the scales of transformational, transactional leadership style and job satisfaction. Organizations should focus on using the transformational leadership style for improving the job satisfaction among their employees.
One of the major limitations of this research is the small sample size, because of which the findings of the study cannot be generalized. Another limitation of this research is associated with the issue of truthfulness of the respondents involved in the study. This can have a potential impact on the results of the survey. The future researches can focus on examining the relationship between the elements of transformational leadership and job satisfaction.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
References
- Aziri, B. (2011), ‘Job satisfaction: A literature review,’ Management Research and Practice,3 (4), 77-86.
- Bass, B. M. (1985) Leadership and Performance Beyond Expectations,Free Press.
- Bektaş, Ç. (2017), ‘Explanation of intrinsic and extrinsic job satisfaction via mirror model,’ Business & Management Studies: An International Journal, 5 (3), 627-639.
- Berson, Y. & Avolio, B. J. (2004), ‘Transformational leadership and the dissemination of organizational goals: A case study of a telecommunication firm,’ The Leadership Quarterly, 15 (5), 625-646.
- Bhatti, N. et al. (2012), ,The Impact of Autocratic and Democratic Leadership Style on Job Satisfaction,’ International Business Research,5 (2), 192-201.
- Burns, J. M. (1978) Leadership,Harper & Row.
- Darshan, G. (2011), ‘Effects of transformational leadership on subordinate job satisfaction in leather companies in Ethiopia,’ International Journal of Business Management & Economic Research, 2 (5), 284-296.
- Goetz, K. et al. (2012), ,The impact of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the job satisfaction of dentists,’ Community dentistry and oral epidemiology,40 (5), 474-480.
- Javed, H. A., Jaffari, A. A. & Rahim, M. (2014), ‘Leadership Styles and Employees’ Job Satisfaction: A Case from the Private,’ Journal of Asian Business Strategy,4 (3), 41-50.
- Khan, J. A. (2011) Research Methodology,APH Publishing.
- Naidu, J. & Walt, M. S. v. d. (2005) ‘An Exploration Of The Relationship Between Leadership Styles And The Implementation Of Transformation Interventions,’ SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 3 (2), 1-10.
- Northouse, P. G. (2015) Leadership: Theory and Practice,7th ed. USA: SAGE Publications.
- Pallant, J. (2016) SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS, 6th ed. London: McGraw Hill/Open University Press.
- Ramos, N. (2014),’Transformational Leadership and Employee Job Satisfaction: The Case of Philippines Savings Bank Batangas Branches,’Asia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary Research,2 (6), 6-14.
- Richter, A. et al. (2016),’iLead—a transformational leadership intervention to train healthcare managers’ implementation leadership,’Implementation Science,11 (1).
- Saleem, H. (2015),’The impact of leadership styles on job satisfaction and mediating role of perceived organizational politics,’Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences,172, 563-569.
- Sarwar, A., Mumtaz, M., Batool, Z. & Ikram, S. (2015),’Impact of Leadership Styles on Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment,’International Review of Management and Business Research, 4 (3), 834-844.
- Valentine, Godkin, Fleischman & Kidwell (2011),’Corporate Ethical Values, Group Creativity,Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention: The Impact of Work Context on Work Response,’Journal of Business Ethics,98 (3), 353-372.
- Voon, M., Lo, M., Ngui, K. & Ayob, N. (2011),’The influence of leadership styles on employees’ job satisfaction in public sector organizations in Malaysia,’International Journal of Business, Management and Social Sciences,2(1), 24-32.
- Weiss, D. J. & Dawis, R. V. (1967)Manual for the Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire, Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.











